In the evolving landscape of modern employment, technical expertise alone no longer guarantees professional success. Soft skills—interpersonal abilities, emotional intelligence, and effective communication—are essential for fostering collaboration, innovation, and adaptability in diverse work environments. As organizations prioritize holistic talent acquisition, soft skills assessment has emerged as a vital tool to evaluate and develop these competencies effectively. It is useful as a standalone assessment but also to provide incremental validity over cognitive assessments.
This article explores the significance of soft skills, their impact on professional development, and strategies for assessing and cultivating them, supported by recent research and expert insights. If you are ready to implement these assessments, you can purchase pre-made assessments from companies like ioPredict, or leverage ASC’s test development services and online assessment platform to develop and deliver your own.
What Are Soft Skills?
Soft skills encompass a broad range of interpersonal and intrapersonal competencies. Unlike hard skills, which are technical and measurable, soft skills include attributes such as:
- Communication: The ability to articulate ideas clearly and listen actively.
- Teamwork: Collaborating effectively with individuals from diverse backgrounds.
- Adaptability: Responding positively to change and managing uncertainty.
- Emotional Intelligence (EI): Recognizing and managing one’s emotions and understanding others’ feelings.
- Problem-Solving: Addressing challenges with creativity and critical thinking.
These competencies enable individuals to navigate complex interpersonal dynamics and adapt to evolving professional demands.
Why Are Soft Skills Critical?
Enhanced Workplace Collaboration
Organizations are increasingly team-oriented, necessitating effective interpersonal communication and cooperation. Research from McKinsey & Company (2021) highlights that teams with strong collaborative skills outperform their counterparts by 25% in productivity.
Adaptability in a Changing World
In an era defined by technological disruption and remote work, adaptability has become a cornerstone of professional success. A study by the World Economic Forum (2020) emphasized adaptability as a top skill for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Leadership and Emotional Intelligence
Leadership transcends technical knowledge; it’s about inspiring and guiding teams. Emotional intelligence, a core soft skill, has been linked to effective leadership. According to Daniel Goleman’s seminal work on EI, leaders with high emotional intelligence are more likely to foster employee engagement and retention (Goleman, 1998).
Improved Customer Relations
For customer-facing roles, soft skills such as empathy and active listening are critical. A Salesforce study (2022) found that 70% of customers are more likely to remain loyal to businesses where they feel understood and valued.
Approaches to Assessment of Soft Skills
Assessing soft skills requires tools and methods that simulate real-world challenges and measure an individual’s behavioral responses. A well-designed soft skills assessment program provides actionable insights into candidates’ and employees’ abilities to thrive in complex workplace environments. Here are some common methods of assessment: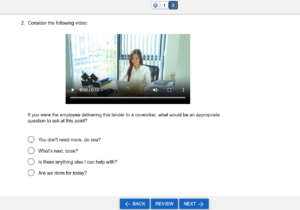
- Situational Judgment Tests (SJTs): Candidates are presented with realistic workplace scenarios and asked to choose the best course of action, revealing their decision-making and interpersonal abilities. An example of this on ASC’s assessment platform is seen on the right.
- Behavioral Interviews: Structured questions that prompt candidates to describe past experiences and how they managed specific situations.
- 360-Degree Feedback: Collecting input from colleagues, supervisors, and subordinates to gauge interpersonal effectiveness.
- Personality and Emotional Intelligence Assessments: Tools like the Big Five measure traits that impact communication and adaptability, as well as other important attributes like conscientiousness or integrity.
- Workplace Simulations: Role-playing exercises that mirror day-to-day challenges in the role.
Example Questions for Soft Skills Assessment in an Interview
Communication: “Describe a time when you had to explain a complex idea to someone who didn’t have the same knowledge as you. How did you ensure they understood?”
Teamwork: “Tell me about a time you worked on a team project. What was your role, and how did you handle disagreements?”
Adaptability: “Can you share an experience where you had to adjust to significant changes in your workplace? How did you handle it?”
Problem-Solving: “Describe a challenging problem you faced at work. How did you identify the root cause and resolve it?”
Emotional Intelligence: “Give an example of a situation where you recognized someone’s emotions were affecting their performance. How did you address it?”
Assessing Soft Skills in Formal Assessments
Many soft skills can also be assessed with standardized tests. The aforementioned example of a situational judgment test is one case of these. Here is an example of an SJT item to assess communication and customer service skills.
You are working as a customer service representative at a retail store. A customer approaches the counter, visibly upset. They begin shouting at you, complaining that they purchased an item a week ago, but it’s now broken, and they want a full refund. Despite your calm and polite responses, the customer continues to escalate, demanding to speak to your manager.
What would be the most appropriate course of action in this situation?
A) Stay calm, listen to the customer’s concerns, and offer a solution such as a replacement or repair, explaining the store’s return policy. If the customer insists on speaking to a manager, politely refer them to your manager.
B) Apologize for the inconvenience, assure the customer that you will immediately issue a full refund without checking the product’s condition, to avoid further conflict.
C) Respond in a firm, but professional tone, telling the customer that they are being unreasonable and need to calm down before any solution can be discussed.
D) Ignore the customer’s outburst and proceed with the next transaction, hoping they will calm down on their own.
Developing Soft Skills
Soft skills can be cultivated through deliberate practice, feedback, and training. Here are some effective strategies:
Continuous Learning
Investing in personal development through workshops, online courses, and seminars can enhance soft skills. Platforms like Coursera and LinkedIn Learning offer courses on communication, emotional intelligence, and leadership.
Feedback and Reflection
Constructive feedback from peers, mentors, and supervisors provides insights into areas for improvement. Reflection on workplace interactions further aids self-awareness.
Role-Playing and Simulations
Role-playing exercises and situational judgment tests simulate real-world scenarios, allowing individuals to practice and refine their responses.
Mentorship Programs
Learning from experienced mentors can provide valuable perspectives on navigating workplace challenges and building meaningful relationships.
Mindfulness and Emotional Regulation
Practices such as mindfulness meditation enhance emotional regulation, a key component of emotional intelligence. Studies by Harvard Medical School (2018) suggest that mindfulness training improves focus, empathy, and stress management.
Measuring the Impact of Soft Skills
While soft skills are intangible, their impact is quantifiable through various metrics at a business level.
Employee Retention: Organizations that invest in soft skills training report lower turnover rates (LinkedIn Workplace Learning Report, 2023).
Team Performance: Teams with strong communication and collaboration skills achieve higher project success rates (MIT Sloan Management, 2017).
Customer Satisfaction: Enhanced interpersonal skills lead to improved client relationships and customer loyalty.
Conclusion
Soft skills are no longer supplementary but integral to professional success. Through robust soft skills assessment strategies, organizations can identify and nurture these critical competencies, ensuring long-term growth and innovation. Whether through improved collaboration, adaptability, or leadership, soft skills remain the foundation of sustainable success in today’s complex workplace environments.
References
- McKinsey Global Surveys: A year in review. (2021).
- World Economic Forum. (2020). “The Future of Jobs Report 2020.”
- Goleman, D. (1998). Working with Emotional Intelligence. Bantam Books.
- Harvard Medical School. (2018). “Mindfulness Practices and Their Impact on Workplace Stress Management.”
- Salesforce Research. (2022). “Customer Engagement Research.”
- LinkedIn Workplace Learning Report. (2023).
- MIT Sloan Management. (2017). “Soft skills training brings substantial returns on investment.”

