Nathan Thompson articles

Three Approaches for IRT Equating
IRT equating is the process of equating test forms or item pools using item response theory to ensure that scores are comparable no matter what set of items that an examinee sees. If you are

Power of linear on the fly testing
Linear on the fly testing (LOFT) is an approach to assessment delivery that increases test security by limiting item exposure. It tries to balance the advantages of linear testing (e.g., everyone sees the same number
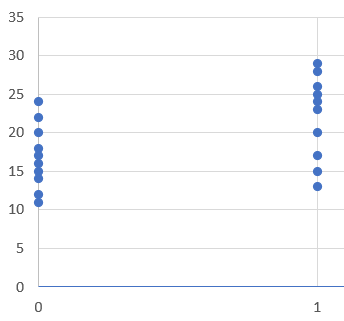
Item-total point-biserial correlation
The item-total point-biserial correlation is a common psychometric index regarding the quality of a test item, namely how well it differentiates between examinees with high vs low ability. What is item discrimination? While the word
CalHR Selects Assessment Systems as Vendor for Personnel Selection
The California Department of Human Resources (CalHR, calhr.ca.gov/) has selected Assessment Systems Corporation (ASC, assess.com) as its vendor for an online assessment platform. CalHR is responsible for the personnel selection and hiring of many job roles for

Learn About Tech Innovation With Dr. Nathan Thompson On The EdNorth EdTech Podcast
Nathan Thompson, Ph.D., was recently invited to talk about ASC and the future of educational assessment on the Ednorth EdTech Podcast.EdNorth is an association dedicated to continuing the long history of innovation in educational technology

What is a Standard Setting Study?
A standard setting study is a formal process for establishing a performance standard. In the assessment world, there are actually two uses of the word standard - the other one refers to...
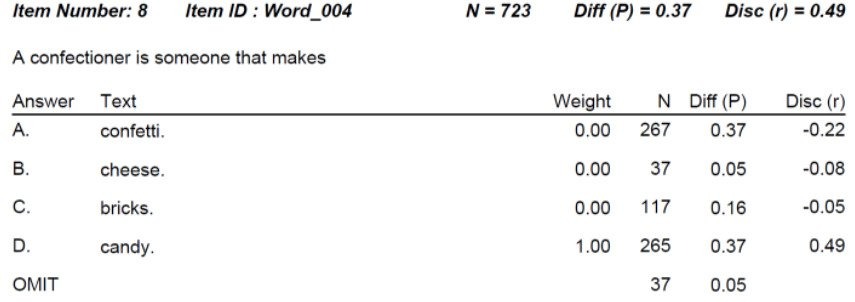
Item Analysis in Psychometrics: Improve Your Test
Item analysis is the statistical evaluation of test questions to ensure they are good quality, and fix them if they are not. This is a key step in the test development cycle; after items have

Seven Technology Hacks to Deliver Assessments More Securely
So, yeah, the use of “hacks” in the title is definitely on the ironic and gratuitous side, but there is still a point to be made: are you making full use of current technology to
The IACAT Journal: JCAT
Do you conduct adaptive testing research? Perhaps a thesis or dissertation? Or maybe you have developed adaptive tests and have a technical report or validity study? I encourage you to check out the Journal of Computerized
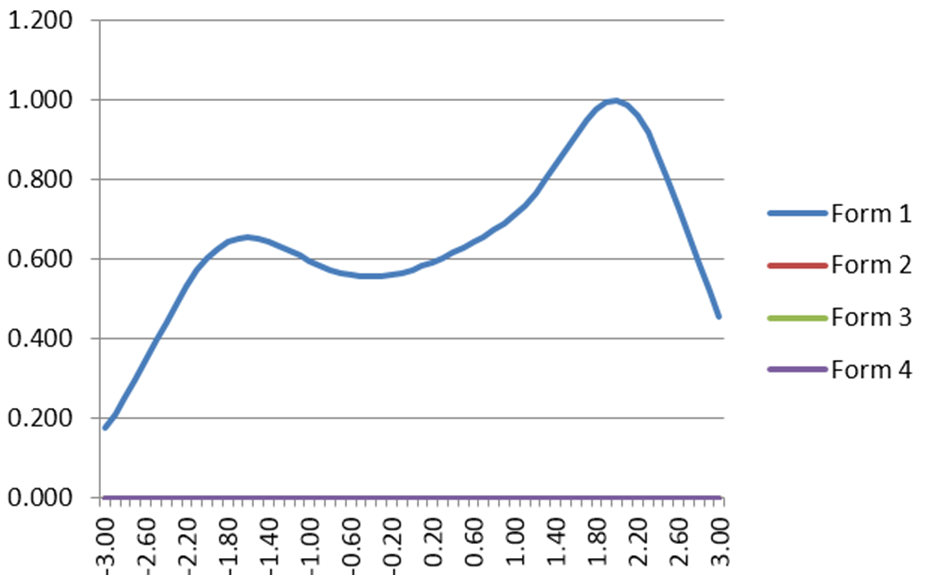
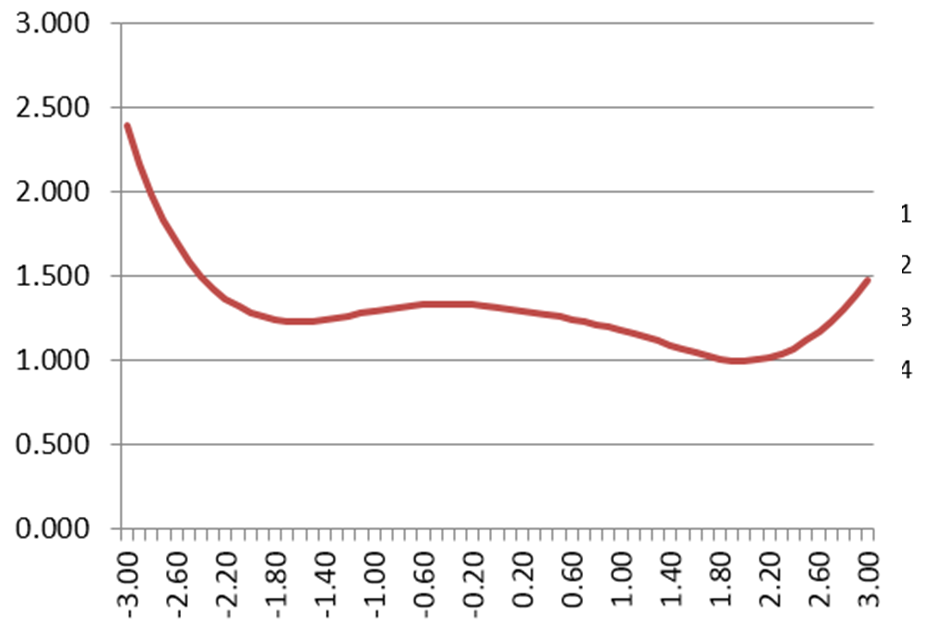
IRT Test Information Function
The IRT Test Information Function is a concept from item response theory (IRT) that is designed to evaluate how well an assessment differentiates examinees, and at what ranges of ability. For example, we might expect
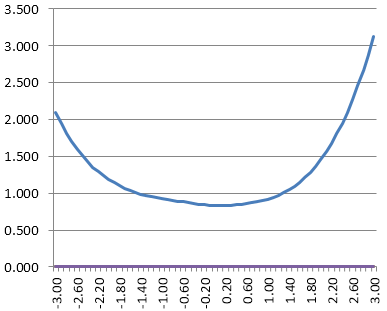
What Is The Standard Error of Measurement?
The standard error of measurement (SEM) is one of the core concepts in psychometrics. One of the primary assumptions of any assessment is that it is accurately and consistently measuring whatever it is we want

Question Banks: An Introduction
What is a question bank? A question bank refers to a pool of test questions to be used on various assessments across time. ..

Psychometrist: What do they do?
A psychometrist is a professional that specializes in how to deliver and interpret clinical psychological and educational assessments. That is, they work in a one-on-one clinical situation. For example, they might give IQ tests to

What is Classical Item Difficulty (P Value)?
One of the core concepts in psychometrics is item difficulty. This refers to the probability that examinees will get the item correct for educational/cognitive assessments or respond in the keyed direction with psychological/survey assessments (more on that

Item Banks: 6 Ways To Improve
The foundation of a decent assessment program is the ability to develop and manage strong item banks. Item banks are a central repository of test questions, each stored with important metadata such as Author or

Responses in Common (RIC) Index
This collusion detection (test cheating) index simply calculates the number of responses in common between a given pair of examinees. For example, both answered ‘B’ to a certain item regardless of whether it was correct

Exact Errors in Common (EEIC) collusion detection
Exact Errors in Common (EEIC) is an extremely basic collusion detection index simply calculates the number of responses in common between a given pair of examinees. For example, suppose two examinees got 80/100 correct on

Errors in Common (EIC) Exam Cheating Index
This exam cheating index (collusion detection) simply calculates the number of errors in common between a given pair of examinees. For example, two examinees got 80/100 correct, meaning 20 errors, and they answered all of
