Psychometrics

Tips to Improve Test Publishing Quality Control
Test publishing is the process of preparing computer-based assessments for delivery on an electronic platform. Test publishing is like a car rolling off the assembly line. It’s the culmination of a great deal of effort

What is a testlet?
Testlet is a term in educational assessment that refers to a set of test items or questions grouped together on a test, often with a common theme or scenario. This approach aims to provide a

Job Task Analysis Study: Why essential for Certification?
Job Task Analysis (JTA) is a formal process to define what is being done in a profession, especially what is most important or frequent, and then using this information to make data-driven decisions. It is

Four-Fifths Rule: Fair Employment Selection
The Four-Fifths Rule is a term that refers to a guideline for fairness in hiring practices in the USA. Because tests are often used in making hiring decisions, the Four-Fifths Rule applies to them so
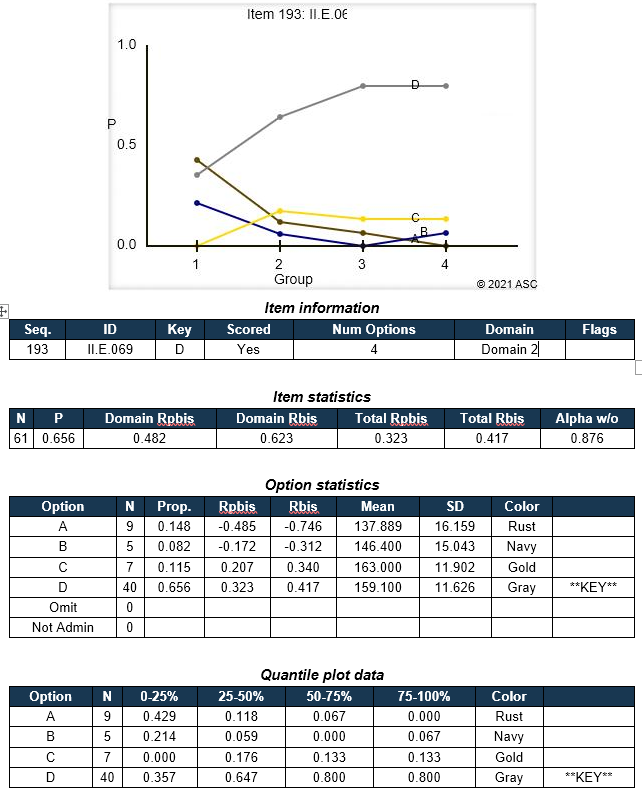
Classical Test Theory: Item Statistics
Classical Test Theory (CTT) is a psychometric approach to analyzing, improving, scoring, and validating assessments. It is based on relatively simple concepts, such as averages, proportions, and correlations. One of the most frequently used aspects

Content Validity in Assessment
Content validity is an aspect of validity, a term that psychometricians use to refer to evidence that interpretations of test scores are supported. For example, predictive validity provides evidence that a pre-employment test will predict

Predictive Validity of Test Scores: Why so Critical for Pre-Employment and Higher Education?
Predictive Validity is a type of test score validity which evaluates how well a test predicts a future variable, and serves as evidence that the test is therefore useful for this purpose. For instance, it

Classical Test Theory vs. Item Response Theory
Classical Test Theory and Item Response Theory (CTT & IRT) are the two primary psychometric paradigms. That is, they are mathematical approaches to how tests are analyzed and scored. They differ quite substantially in substance

All Psychometric Models Are Wrong
The British statistician George Box is credited with the quote, “All models are wrong but some are useful.” As psychometricians, it is important that we never forget this perspective. We cannot be so haughty as

The Graded Response Model – Samejima (1969)
Samejima’s (1969) Graded Response Model (GRM, sometimes SGRM) is an extension of the two parameter logistic model (2PL) within the item response theory (IRT) paradigm. IRT provides a number of benefits over classical test theory,
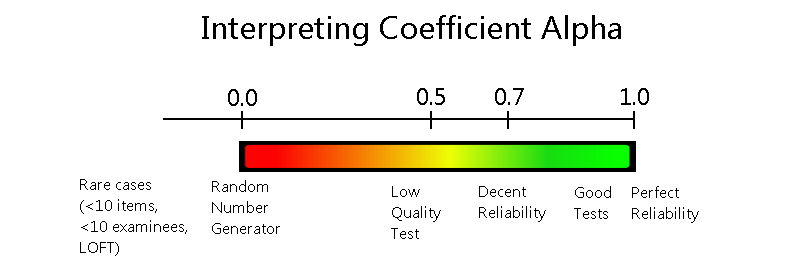
Coefficient Alpha Reliability Index
Coefficient alpha reliability, sometimes called Cronbach’s alpha, is a statistical index that is used to evaluate the internal consistency or reliability of an assessment. That is, it quantifies how consistent we can expect scores to
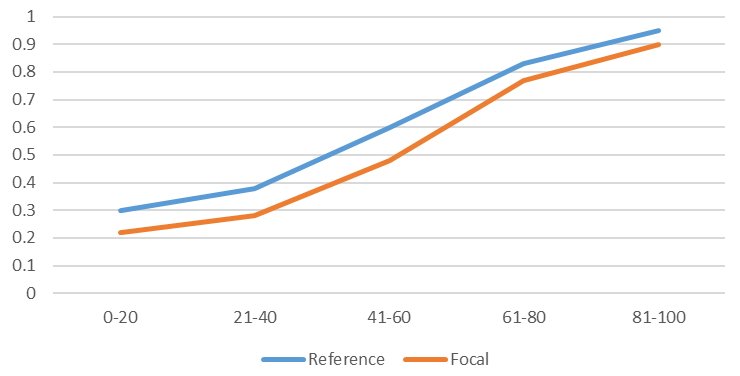
Differential Item Functioning (DIF)
Differential item functioning (DIF) is a term in psychometrics for the statistical analysis of assessment data to determine if items are performing in a biased manner against some group of examinees. This analysis is often

“Dichotomous” Vs “Polytomous” in IRT?
What is the difference between the terms dichotomous and polytomous in psychometrics? Well, these terms represent two subcategories within item response theory (IRT) which is the dominant psychometric paradigm for constructing, scoring and analyzing assessments.

How do I develop a test security plan?
A test security plan (TSP) is a document that lays out how an assessment organization address security of its intellectual property, to protect the validity of the exam scores. If a test is compromised, the
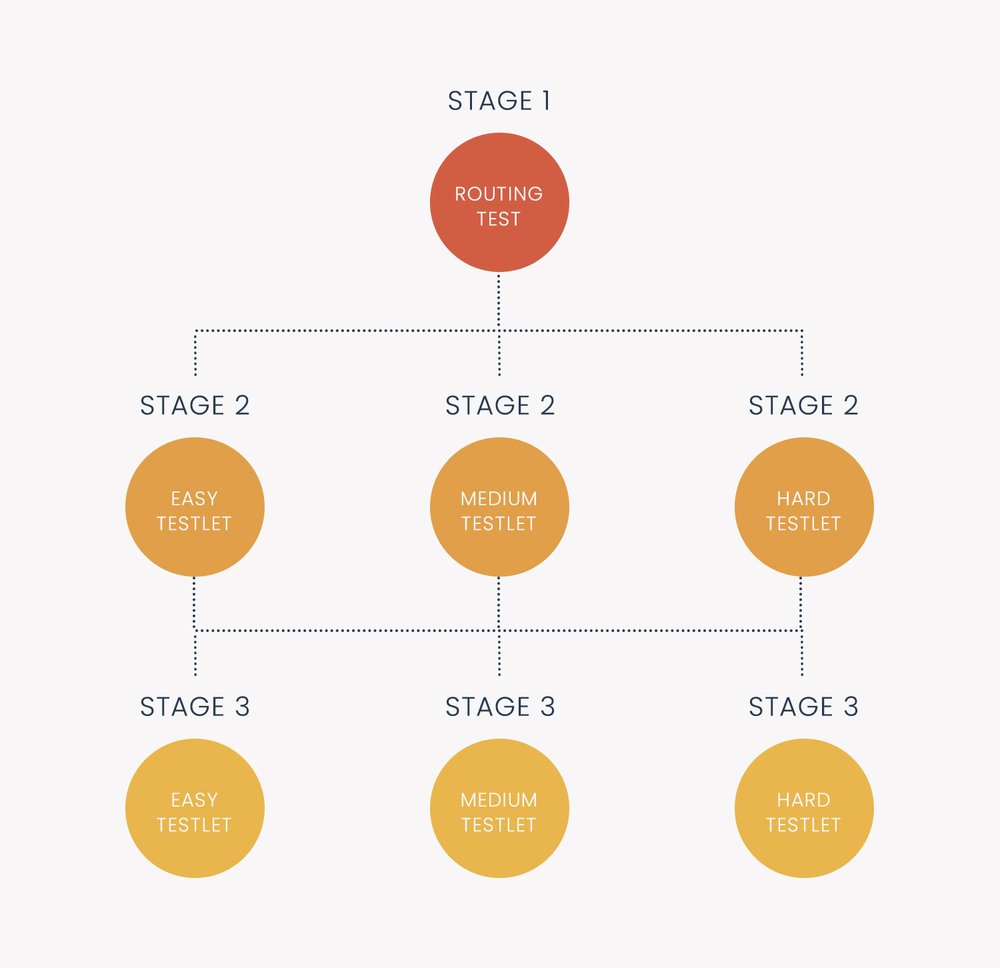
Multistage Testing
Multistage testing (MST) is a type of computerized adaptive testing (CAT). This means it is an exam delivered on computers which dynamically personalize it for each examinee or student. Typically, this is done with respect

Maximum Likelihood Estimation
Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) is an approach to estimating parameters for a model. It is one of the core aspects of Item Response Theory (IRT), especially to estimate item parameters (analyze questions) and estimate person
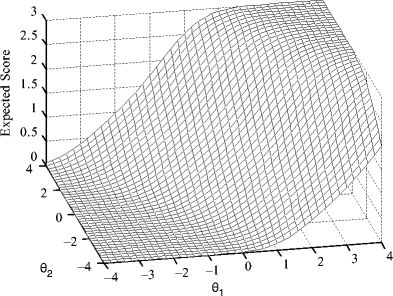
Multidimensional Item Response Theory
Multidimensional item response theory (MIRT) has been developing from its Factor Analytic and unidimensional item response theory (IRT) roots. This development has led to an increased emphasis on precise modeling of item-examinee interaction and a

The IRT Item Pseudo-guessing c Parameter
The item pseudo-guessing parameter is one of the three item parameters estimated under item response theory (IRT): discrimination a, difficulty b, and pseudo-guessing c. The parameter that is utilized only in the 3PL model is
